High current with parallel LM338 - Electronic Project
Introduction:
The variable resistor in the circuit diagram above is used to represent the actions of a current regulator project system. We will assume the variable resistor is Power supply automated and can auto-adjust its own resistance. When the circuit is powered, the variable resistor adjusts its resistance to compensate for changes in the current due to variations in load resistance or voltage supply. From basic electricity class, you should remember that when the load, which is essentially resistance (+ capacitance/inductance) is increased, an effective drop in current is experienced and vice versa.
Thus when the load in the circuit diagram is increased (increase in resistance), rather than a current drop, the Circuit diagram variable resistor reduces its own resistance to compensate for the power supply's increased resistance and ensure the same current flows. In the same way, when the Currenttlou load resistance reduces, the variable resistance increases its own resistance to compensate for the project system reduction, thus maintaining the output current value. Another approach in current regulation is to connect a sufficiently Power supply high resistor in parallel with the load such that, as in line with the laws of basic electricity, as current will flow through the path with the currently least resistance which in this case will be through the Circuit diagram load, with only a "negligible" amount of current flowing through the Project system high-value resistor.
LM317s are designed in such a way that the regulator keeps adjusting its voltage until the voltage between its output pin and its adjustment pin is at 1.25v and as such a divider is usually used when implementing in a power supply voltage regulator situation. But for our use case as a current power supply regulator, it actually makes things super easy for us because, since the Circuit diagram voltage is constant, all we need to do to make the Project system current constant is to simply insert a resistor in series between the project system Vout and ADJ pin as shown in the circuit diagram above. As such, we are able to set the output current to a fixed value which is given by;
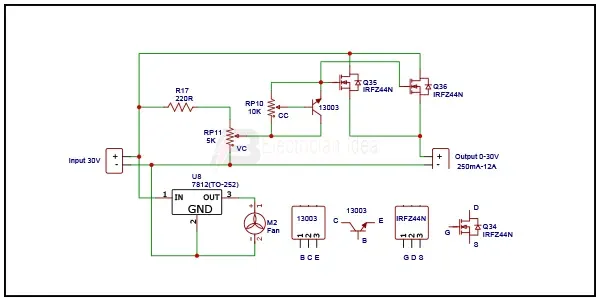
Diagram of High current adjustable voltage regulator circuit, 0-30V 20A:
Components Needed for this Project:
You can get the components from any of the sites below:
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
*Please note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
Read Also:
- 5v regulator 7805 upgrade to 10a
- 5v voltage regulator
- ac 240v to ac 120v converter
- adjustable power supply 48v 60a
- adjustable voltage and current regulator circuit
Working Principle of 0-30V 20A High current adjustable voltage regulator circuit:
The variable resistor in the circuit diagram above is used to represent the actions of a current regulator Project System. We will assume the variable resistor is automated and can auto-adjust its power supply resistance. When the circuit is powered, the variable resistor adjusts its resistance to compensate for changes in the current due to variations in load resistance or voltage supply. From basic electricity class, you should remember that when the load, which is essentially resistance (+ capacitance/inductance) is increased, an effective drop in current is experienced and vice versa. Thus when the load in the circuit is increased (increase in resistance), rather than a current drop, the variable resistor reduces its own resistance to compensate for the increased resistance and ensure the same current flows.
In the same way, when the load resistance reduces, the project system the variable resistance increases its own resistance to compensate for the Circuit diagram reduction, thus maintaining the power supply output current value. Another approach in current regulation is to connect a power supply sufficiently high resistor in parallel with the Currenttlou load such that, in line with the laws of basic electricity, as current will flow through the path with the Project system's least resistance which in this case will be through the power supply load, with only a "negligible" as the amount of current flowing through power supply the high-value resistor.
For the design of current regulators using IC-based voltage regulators, the technique usually involves setting up voltage regulators to have a constant load resistance Linear voltage regulators are usually used because, the voltage between the output of linear regulators and their ground is usually tightly regulated, as such, a fixed resistor can be inserted between the terminals such that a fixed current flows to the load.
the voltage between its output pin and its adjustment pin is at 1.25v and as such a divider is usually used when implementing a voltage regulator situation. But for our use case as a current regulator, project system it actually makes things super easy for us because, since the voltage is constant, all we need to do to make the current constant is to simply insert a Power supply resistor in series between the Vout and ADJ pin as shown in the circuit diagram above. As such, we are able to set the output current to a fixed value which is given by.
The shunt, which is essentially a low-value resistor, Project system is used to measure the current flowing through the Circuit diagram load. When the circuit is switched on, as a voltage drop is noted across the Currenttlou shunt. The higher the value of the load resistance RL the higher the voltage drop across the shunt. The voltage drop across the shunt acts as a trigger for the control transistor such that the higher the voltage drop across the shunt, the more the transistor conducts and regulates the Circuit diagram bias voltage applied to the base of the power supply transistor to increase or reduce conduction with the Project system resistor R1 acting as the bias resistor.
Frequently Asked Questions
An adjustable voltage regulator produces a DC output voltage, which can be adjusted to any other value of a certain voltage range. Hence, the adjustable voltage regulator is also called a variable voltage regulator. The DC output voltage value of an adjustable power supply voltage regulator can be either positive or Circuit diagram negative.
Those are voltage regulators of fixed positive, fixed negative, and adjustable types. By using the fixed voltage regulators Circuit diagram, we will get the fixed output voltage either Power supply positive or negative. Whereas by using adjustable voltage regulators we can get the Circuit diagram desired output voltage within a range of power supply voltages.
An adjustable voltage regulator produces a DC output voltage, which can be adjusted to any other value of a certain voltage range. Hence, the adjustable voltage regulator is also called a variable voltage regulator. The DC output voltage value of an adjustable Circuit diagram voltage regulator can be either positive or negative.
In modern keyboards and synthesizers, a control voltage pedal (or other controlling device) Project system can be used to manipulate certain parameters, which, in the Circuit diagram case of a pedal, would leave the player's hands-free to play the keyboard. In these cases, the pedal usually doesn't generate the voltage.
High-power supply compensation type: The advantages are good anti-interference and performance, high voltage regulation accuracy Circuit diagram, fast response, and a simple circuit diagram. Disadvantages: the input current has large distortion, the Power supply source power supply factor is low, and the output voltage has a phase shift to the Circuit diagram input voltage.

Post a Comment
Do leave your comments