1.5V Step-up Switching regulator circuit - Electronic Project
Introduction:
It is an important power supply component in all switching regulator circuit diagrams. In the datasheet, it states 170uH, 220uH, 100uH. Some people have problems using it or can’t find it. We are the same. But keep in mind that it’s a coil. It’s that simple! We try to wrap the wires on the power supply ferrite core. Then try it! It turned out to be as good as it seems. Look at below. For example ferrite core that we use. It is most commonly found in compact fluorescent lamps.
In many technical applications, a Project system is required to convert a set voltage DC source into a Power supply variable-voltage DC output. A DC-DC switching converter converts the voltage project system directly from DC to DC and is simply known as a DC Converter Circuit diagram. A DC converter is equivalent to an AC transformer with a continuous power supply variable turns ratio. It can be used to step down or step up a DC voltage Project system source, as a transformer.
DC converters are widely used for traction motor control in electric Project system automobiles, trolley cars, marine hoists, forklift trucks, and mine haulers. They provide high efficiency, good acceleration Power supply control, and fast dynamic Currenttlou response. They can be used in the regenerative braking of DC motors to return energy back into the supply. This attribute results in energy savings for transportation Project systems with frequent steps. DC converters are used in DC voltage regulators; and also are used, with an inductor in Circuit diagram conjunction, to generate a DC current source, as specifically for the project system current source inverter.
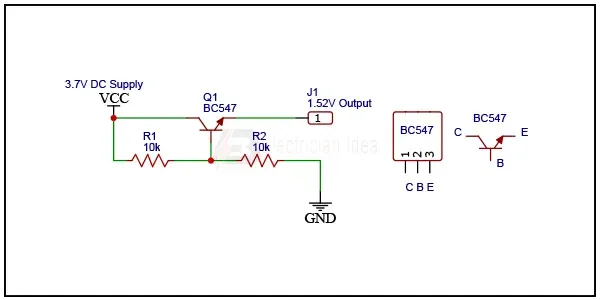
Diagram of USB 5V to 1.5V/ 3V Step Down Converter Circuit:
Components Needed for this Project:
You can get the components from any of the sites below:
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Name [See Buy Click Amazon]
*Please note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
Read Also:
- 12v auto cut off battery charger
- 12v charging indicator circuit
- 12v dc fan speed controller
- 12v negative voltage regulator
- 12v to 220v inverter
Working Principle of USB 5V to 1.5V/ 3V Step Down Converter:
Many times, there is a need to step up or step down DC voltages. The circuit diagram for stepping up or stepping down DC voltages is not as simple as the power supply case with AC voltages. The level changing of DC voltages requires a complex circuitry diagram. These circuits are called DC-to-DC converters. The DC–DC converters are the electronic circuits that convert a constant DC voltage to a high voltage level or to a low voltage level.
When a circuit increases the DC voltage to a higher level, it is called a Boost Converter. When a circuit decreases DC voltage to a lower level, it is called a buck converter. Since a boost converter converts the DC voltage to a higher voltage level, it is also known as a step-up converter. For boosting the power supply voltage signal a regulator circuit diagram is required which can step up the current input voltage signal.
Most electronic gadgets like smartphones, and tablets work on 5V DC. However, for general-purpose use, 3.7 V batteries are quite common. These batteries can be used to power supply up to 5V devices using a boost converter circuit diagram. In this electronics project, the voltage from the 3.7 V Li-ion battery is boosted to 5V DC. The end-of-discharge voltage of the Li-ion battery can be assumed 3.5 V so this circuit will convert the minimum input voltage of 3.5 V to 5V level. A maximum current of 500 mA can be drawn by this Project system boost converter. The regulator used for boosting the signal in this project system is MC34063AP1 which will step up the Currenttlou input signal to the desired voltage level.
In order to eliminate any AC noise or the ripple that transistorized switch motion generates, the output capacitor is placed between the two ends of the output of the switching regulator circuit. The inductor and output capacitor form together and can make most transistor switch noise can not arrive at the " low pass " filter of load. With respect to the resonance frequency of filter " LC " resonant tank (tank), switching frequency (being generally 1MHz or bigger) is necessary for " height ".
Through a plurality of switch periods, averaging, the switchable inductor is the running of a programmable current source (behave) of the average current with a slow variation. If the transistor switch incident (promptly; With MOSFET from by switching to the time that conducting spends; Vice versa) compares shorter relatively with the time period between each switch event; Then in circuit analysis, can the energy loss during the switch be thought insignificantly, also or with it see the energy loss that fixes. Yet at the switching frequency place of several megahertzes.
Frequently Asked Questions
The actual answer is YES, Circuit Diagram, and NO. Depends. If your device uses only 1 A, then you can't use it, because this Project system battery puts out 3.7 V instead of 1.5 V. If your device uses 2 A Circuit diagram batteries, then you can use it IF you Circuit diagram substitute a dummy battery for 1 of the 1.5 V batteries.
Can I use 1.2 V rechargeable batteries in devices that Circuit diagram usually takes 1.5 V throw-away batteries. Yes, most definitely. Using 1.2 V rechargeable batteries will have no effect on the current use of the equipment. In fact, an alkaline battery only benefits from 1.5 V voltage at the project system beginning of its discharge.
The easiest way to convert a 5V analog signal to a 3.3V analog Project system signal is to use a resistor divider with an R1:R2 ratio of 1.7:3.3 Circuit diagram. However, there are some problems with this approach. 1) The attenuator may be connected to a capacitive load project system, forming an undesired low-pass filter.
You can use a boost converter. This is a circuit composed of oscillator, switching transistor, diode, and an inductor/capacitor. Usually, there is a feedback element to regulate the Project system output voltage. The inductor performs the Power supply voltage boost.
If you are talking about a resistive load or a device that has an internal regulating device, the 5 Volt, 2 Ampere power supply is close enough and just fine to use. However, if the device in question is a battery, especially a Lithium Ion battery, using anything besides the manufacturer's power supply IS dangerous!

Post a Comment
Do leave your comments