Non Frost Refrigerator wiring | refrigerator circuit wiring
Non Frost Refrigerator wiring:
This Diagram shows The No Frost Technology Automatically adjusts and Controls the Temperature and Humidity levels inside the Refrigerator. This technical Solution prevents frost from occurring on the food Products by Means of Proper air Circulation and drying. The Cavity of The Fridge is Then Precisely Ventilated. A Fridge With No Frost Extracts Both The air as well as any Humidity From The Freezer Compartment. Because of This, The Humidity Freezes outside of The Freezer Compartment.
Diagram of Non Frost Refrigerator wiring:
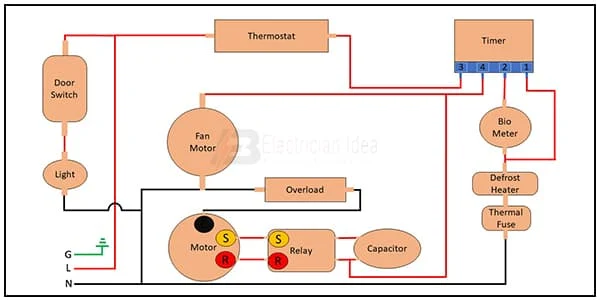 |
| Fig 1: Non Frost Refrigerator wiring |
Components Need for this Project:
You can get the components from any of the sites below:
- Door Switch [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Thermostate [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Timer [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Fan Motor [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Overload [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Capacitor [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Defrost Heter [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Thermal Fuse [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Biometer [See Buy Click Amazon]
*Please note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
$ads={1}Read Also:
Components used to make the Non Frost Refrigerator wiring:
01. Door Switch
 |
| Fig 2: Door Switch |
We understand that someone has come home after hearing the sound of the doorbell or calling the bell. Usually, the doorbell is installed at the main gate of the house. According to the scriptures, the importance of sound in the vast of all the sounds we hear around us is discussed in detail. It is believed that just as noisy sounds have a bad effect on our minds, so sweet sweet sounds have a good effect on us. Beautiful sounds have a positive effect on our minds and make our surroundings beautiful. Find out today how doorbells affect our home environment.
02. Thermostate
 |
| Fig 3: Thermostate |
Thermostat is the control device of fridge/refrigerator. which directly or indirectly controls one or more heat sources and cooling systems to maintain the refrigerator's required temperature. A thermostat is a discrete mechanical device that changes its state or electrical contact state when a certain temperature setpoint is reached. When the metal capsule is heated, the volume of its contents changes, which pressures the relay membrane through a capillary tube, and when the set temperature is reached, the contacts are closed or opened.
03. Timer
 |
| Fig 4: Timer |
Timer is a specialized type of clock used for measuring specific time intervals.An electromechanical cam timer uses a small synchronous AC motor turning a cam against a comb of switch contacts. This type of timer often has a friction clutch between the gear train and the cam, the cam can be turned to reset the time.A simple example of the first type is an hourglass. Working method timers have two main groups: hardware and software timers.Most timers give an indication that the time interval that had been set has expired.
04. Motor
 |
| Fig 5: Motor |
A DC Motor is a device that Converts Electrical energy into Mechanical Energy. A DC motor usually accepts a DC source and converts it into mechanical energy, hence it is called a DC motor. A motor in which a series field coil is connected to the armature is called a series motor. The torque of a series motor depends on the armature current, and field strength. A motor in which the field coil is connected in parallel with the armature is called a shunt motor. The torque of a shunt motor depends on the variation of mains field strength and armature current.
05. Overload
 |
| Fig 6: Overload |
Overload relays are often used to protect the motor from excessive current flow. Overload relays are used to protect the motor from overheating. Besides some specific faults such as phase to phase, phase to ground, etc. overload relay provides protection to the motor. A thermal overload relay works on the principle of bimetallic strip electro-thermal characteristics. When the bimetallic heats up, the trip function in the overload relay turns on and disconnects the power supply to the contactor coil, thus tripping the overload relay and breaking the motor current and saving the motor.
06. Capacitor
 |
| Fig 7: Capacitor |
A capacitor is basically an electric charge storage device or an electrical passive device that can store charge. Its Bengali meaning is "container" which means that holds an electric charge. And the device made by separating the two plates by placing a non-conductive material (Dielectric) between the two conductive plates is called a capacitor. A capacitor consists of a dielectric material between two conductive layers. A capacitor in a circuit stores electrical energy or charge from a source. Another popular name is a condenser.
07. Defrost Heter
 |
| Fig 8: Defrost Heater |
The Defrost Heaters are Used to Melt the Accumulated frost off the Evaporator coil Surfaces and warm the drain pan to allow the Defrost Condensate to exit Down the Drain line Without Refreezing the pan. Defrost Heaters are Commonly located beneath refrigerators and Evaporator coils. You Will Have to Remove any Objects That are in your way such as the Contents of the Freezer, Freezer shelves, Icemaker parts, and Back, the Inside rear, or Bottom Panel.
08. Thermal Fuse
 |
| Fig 9: Thermal Fuse |
A fuse is an electrical, electronic or mechanical device that protects a circuit from excessive current or overload. It also acts as a protector and protects home appliances like refrigerators, televisions, computers from high voltage. There are many types of fuses used but all fuses work the same way. The metal of the fuse is made or designed in such a way that it can carry a very small amount of current. When short-circuited or overloaded, the high-flow current generates thermal heat that melts the fuse's metal or element and creates a gap. This gap interrupts the flow of current in the fuse. Basically this is how a fuse works.
09. Biometer
 |
| Fig 10: Biometer |
Biometrics is a technology where a person is uniquely identified based on their physical and behavioral characteristics. Using this technology, computers can identify the behavioral characteristics and physical structure of people. Anthropometrics or biometrics refers to human-related statistics. Biometrics identification is a widely used identification method in computer science. Biometrics is a scientific and technological authentication method based on biology and is used in data assurance. Using this technology, computers can detect human behavioral characteristics and physical structures. Can allow various tasks to be done after the computer is detected.
Thank You for visiting the website. Keep visiting for more Updates
$ads={2}
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the No Frost system in the refrigerator?
The No Frost technology automatically adjusts and controls the temperature and humidity levels inside the refrigerator. This technical solution prevents frost from occurring on the food products using proper air circulation and drying. The cavity of the fridge was then precisely ventilated.
What is the difference between frost and non-frost refrigerators?
1. Ice Frosting: The main difference is “ice”. Frost Refrigerators let chunky ice grow inside the refrigerator, unlike No- Frost refrigerator. If we need to take out meat or other food stored in the freezer in the refrigerator we need to turn off the switch of the refrigerator.
Which is better frost or No Frost freezer?
One of the biggest advantages of No Frost is that you never have to defrost the freezer again. So you won't have to empty the freezer 5 and 6 times a year and remove the ice.
What are the disadvantages of frost-free freezers?
It saves you the hassle of frost in your fridge but can cause more freezer burn, as your food temperatures fluctuate slightly and that makes it easier for moisture inside your food to escape.
What is the best temperature for a no-f Frost freezer?
The recommended freezer temperature to keep your food safe is at and below 0°F (-18°C), but your freezer may need to be set higher and lower depending on its environment or other factors. The typical freezer factory setting on Whirlpool® refrigerators was a great starting point at the recommended 0°F (-18°C).











Post a Comment
Do leave your comments