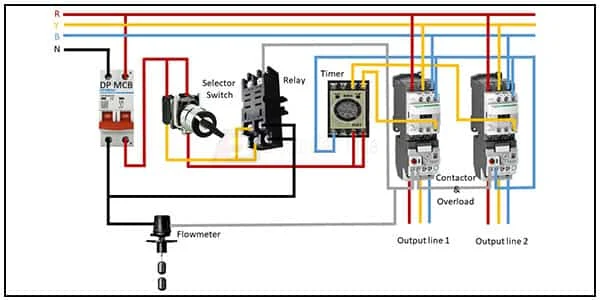
Flowmeter with relay wiring diagram:
This diagram shows how to make flowmeter with relay wiring diagram. In this circuit, we use a DP MCB ( Double Pole Minature Circuit Breaker ), a selelctor switch, a relay, an 8 pin timer, two magnetic contactor, a flowmeter, and two ovreload motor protection relay. Here we need to connect all components prefectly.
Diagram of Flowmeter with relay wiring:
Components Need for this Project:
You can get the components from any of the sites below:
- DP MCB [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Timer [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Relay [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Flowmeter [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Contactor [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Overload [See Buy Click Amazon]
- Selector Switch [See Buy Click Amazon]
Read Also:
Components used to make the flowmeter with relay:
01. DP MCB
 |
| Fig 2: DP MCB |
Double pole MCB can control two wires. This circuit breaker is generally used in single-phase electric lines. Double pole MCB circuit breaker input has two wires supply two wires and an output. In a single-phase line, A double-pole MCB circuit breaker is used to give good production. This circuit breaker is provided through phase and neutral circuit breaker, it is very safe. This circuit breaker is preferred for home appliances. A DP MCB usually trips for 2 reasons 1. Overload 2. Short circuit.
02. Timer
 |
| Fig 3: Timer |
Timer is a specialized type of clock used for measuring specific time intervals.An electromechanical cam timer uses a small synchronous AC motor turning a cam against a comb of switch contacts. This type of timer often has a friction clutch between the gear train and the cam, the cam can be turned to reset the time.A simple example of the first type is an hourglass. Working method timers have two main groups: hardware and software timers.Most timers give an indication that the time interval that had been set has expired.
03. Relay
 |
| Fig 4: Relay |
This relay is known as 8 pin relay because it has 8 terminals. When coil power is supplied. A magnetic induction is created due to which the connected sheet of the Com part moves towards the NO part changing to NO-NC. The former NC region loses conductivity and becomes NO. Thus, as long as power is supplied to the coil, the NO and NC positions will remain in the alternating state, and when the power is removed from the coil, it will return to its original position. This is basically how a relay switch works.
04. Flowmeter
 |
| Fig 5: Flowmeter |
A flow meter is a flow rate measuring device used to determine the linear or nonlinear mass and volumetric flow of a liquid or water. The many names of flow meters include flow water, flow indicator, liquid meter, and flow rate sensor. which can be an open channel or closed conduit. An open channel is when the flow is open to the atmosphere. whereas a closed conduit is when the flow is in a tube or pipe.
05. Contactor
 |
| Fig 6: Contactor |
A magnetic contactor is an electrical device used for load control, automation, and protection. It is much like a magnetic reel. However, relays are generally used for low power and voltage, on the other hand, when we think of high power, these heavy-duty contractors only come to mind. It basically works by switching the load on and off. It has 3 terminals whose inputs are denoted as L1, L2, L3, and outputs as T1, T2, and T3. The circuit of the load is made in automation mode or protection using auxiliary contacts. It has two types of terminals. 1) Normally Open (NO). 2) Normally Closed (NC)
06. Overload
 |
| Fig 7: Overload |
Overload relays are often used to protect the motor from excessive current flow. Overload relays are used to protect the motor from overheating. Besides some specific faults such as phase to phase, phase to ground, etc. overload relay provides protection to the motor. A thermal overload relay works on the principle of bimetallic strip electro-thermal characteristics. When the bimetallic heats up, the trip function in the overload relay turns on and disconnects the power supply to the contactor coil, thus tripping the overload relay and breaking the motor current and saving the motor.
07. Selector Switch
 |
| Fig 8: Selector Switch |
Selector Switches Can be Rotated left, Right, or in The Center in Order to Open or Close The Electrical Contacts. The Function of a Selector Switch is To Control Devices as well as Switch Between a Minimum of Two or More Circuits. The perfect Use For a Selector Switch is When Used for Controlling an Output of a Device. Selector Switches Come as a Complete Unit Often listed as a Terminal Block Meaning the Selector Switch is a Complete Block Which Makes it Simple And easy to Install.
Thank You for visiting the website. Keep visiting for more Updates.

Post a Comment
Do leave your comments